Installing On Linux
First steps
Run as systemd service
1. Create a Unit file to define a systemd service:
vim /lib/systemd/system/aft-extensions-manager.service[Unit]
Description=ExtensionsManager
After=network.target
[Service]
User=root
WorkingDirectory=/usr/local/bin
ExecStart=/usr/local/share/aft-extensions-manager/aft-extensions-manager-linux
Restart=always
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target2. Copy the unit file to /etc/systemd/system and give it permissions:
Start the Service
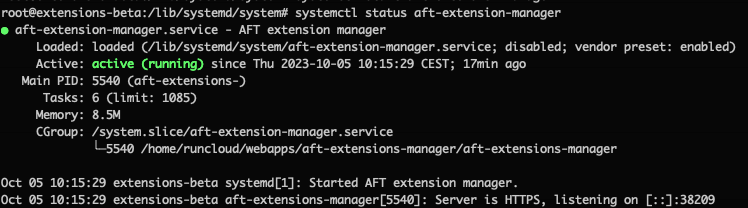
3. The service can be stopped or restarted using standard `systemd` commands:
4. Finally, use the enable command to ensure that the service starts whenever the system boots:
5. Whenever you reboot check the status of the service:

Last updated
Was this helpful?
